Perform initial patient assessment
The initial patient assessment, also referred to as the primary survey, is a critical component of pre-hospital care. This assessment is the basis from which all medical and trauma care decisions are made.
-
(If you have not done so already) Add a new incident, or open an existing incident, as described in Add or edit an incident.
By default, the Response tab and Incident Information sub-tab are selected.
-
Click the Situation tab, and then click the Assessment sub-tab.
An interface for adding a new patient assessment appears on the left side of the interface, and a summary of any assessment information you enter appears at the bottom of the interface. Because you may assess the patient's condition multiple times during treatment, you can record your findings for each of these assessments.
-
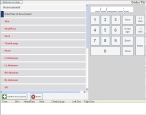
Click Add New Assessment.
The interface updates, and fields for entering assessment information appear on the left side of the interface. The Date/Time of Assessment field is selected by default, and a number pad for entering the time the patient was assessed appears on the right side of the interface.
Note: Through the FH Medic administration site, the FH Medic application can be highly configured to display or hide individual fields, require or not-require fields, and even change field labels. As a result, different fields may appear for you than what is shown in the screen shot.
Information on using the FH Medic administration site to control the fields in the FH Medic application is available in the FH Medic Administrator's Guide .
-
For Date/Time of Assessment, do one of the following.
- Click Now to enter the current system time on your computer.
- Click 5 min ago to enter the current system time on your computer, minus five minutes.
- Click the number buttons to enter a time.
- Adjust the time displayed with the +1 min or -1 min buttons.
-
(Optional, if all or most of the assessments you perform fall within normal limits for the patient) In the upper left corner of the interface, click Within Normal Limits.
All the assessment fields fill in with a value of
Normal. You can override this value for any individual field with the step below. -
For the remaining fields, enter data as described in Understand the interface and data entry in it.
Field Information needed Skin
A description of the patient's skin appearance, temperature, and moisture level, such as pale, cold, and clammy, or mottled and warm.
Head/Face
Any visible injury to the patient's head, such as a mass, lesion, or swelling, and a description of their initial facial features, such as asymmetric smile or droop. Neck
A description of the patient's neck, such as jugular vein distention (JVD),tracheal deviation, the presence of stoma, and so forth.
Chest/Lungs
A description of the patient's chest and lung function, such as symmetrical rising/falling with each breath, the presence of subcutaneous emphysema (SCE, SE, or Sub Q air), stridor, or crepitus upon palpation.
Heart
Pulse rate, character, rhythm, and other information gathered through auscultation with a stethoscope or other cardiac monitoring systems.
LU Abdomen, LL Abdomen,
RU Abdomen,
RL AbdomenAn assessment of all four quadrants of the abdomen for distension, tenderness, a mass, guarding, entrance and exit wounds, evisceration, painful areas, distention, and discoloration.
GU
A description of the condition and any injuries to the patient's genital and urinary systems (kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra).
Back Cervical,
Back Thoracic,
Back Lumbar/SacralPain to range of motion (ROM) in the patient's back, existence of a mass, tenderness in the paraspinal muscles, muscle tightness, and tenderness in the spinous process.
RU Extremities,
RL Extremities,
LU Extremities,
L ExtremitiesA description of any tenderness, swelling, weakness, deformity, contusions, abrasions, buns, bruises, wounds, blood, angulations, abnormal pulses or sensations for the patient.
Left Eye,
Right EyeAn indication of whether the patient's pupils are equal and reactive to light and accommodation (PERLA), discolored, dialated (and how far), or irregular.
Mental Status
An assessment of whether the patient is alert and oriented to time, person, place, and date (A+O x 4), or whether they are confused, hallucinatory, combative, or unresponsive.
Neurological
Evaluation of the patient's nervous system, including gait, cranial muscle tone, posture, speech, tremors,or weakness on one side of the body.